- Faculty of Engineering
- Department of Electronics and Computer Engineering Department of Electrical Systems Engineering Department of Mechanical Systems Engineering Department of Intelligent Mechanical Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Department of Architectural Engineering
- Faculty of Applied Information Science
- Department of Computer Science Department of Information and Communication Department of Information Systems and Management
- Faculty of Environmental Studies
- Department of Architectural Design Department of Global Environment Studies
- Faculty of Life Sciences
- Department of Clinical Engineering Department of Food Sciences and Biotechnology
- Graduate School
- Major in Intelligent Structure and Functional Science Major in Electrical and Electronic Engineering Major in Mechanical Systems Engineering Major in Civil and Architectural Engineering Major in Information Systems Science Major in Environmental Studies Major in Biological and Biomedical Engineering
Faculty of Engineering
Department of Electronics and Computer Engineering
- Department Introduction
- Education and Research Areas
- Subject Introduction
- Curriculum
- Careers and Further Study
- Department Introduction MOVIE
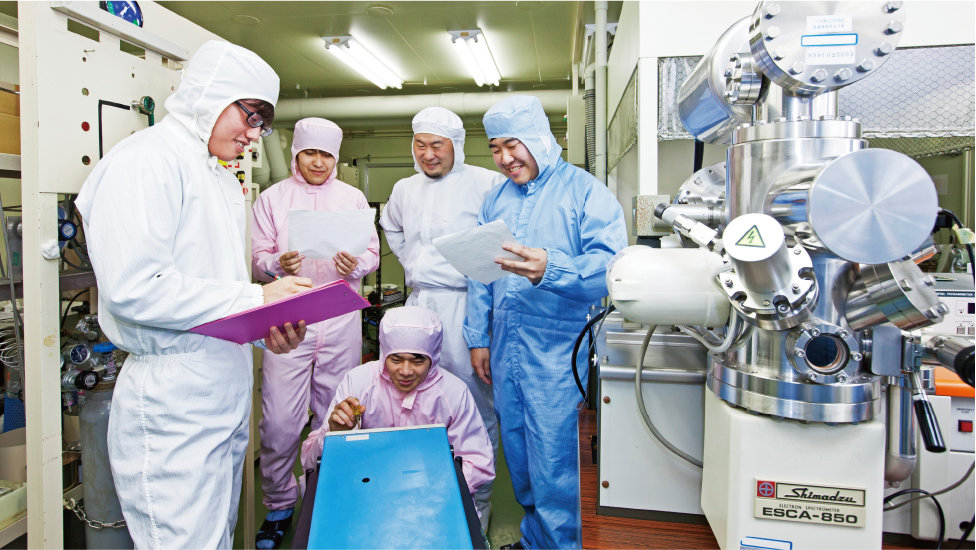

Producing tomorrow’s leading engineers in cutting-edge electronics and computer technology.
Home devices that can be remotely operated by smartphone. Cars which can drive themselves. Every day our society is evolving and changing with the help of electronics and information technology. In the Department of Electronics and Computer Engineering, students are equipped to engage with the ICT-driven development of society by studying cutting-edge electronics and information technology in the three key areas of electronic devices, circuits and telecommunications, and information networks.
Education and Research Areas
-
Electronic Devices
Electronic devices underpin our electronics and information/telecommunications-driven society and are found in a broad range of areas, including in our personal computers and other household electric appliances, in our automobiles and public transport, and in our buildings and homes. Manufacturing these electronic devices requires the use of component material processing technology, design technology and applied technology. Students are therefore equipped with specialized knowledge which allows them to understand the physical characteristics and system design of the electronic devices used in a variety of different systems.
-
Circuits and Telecommunications
Circuit design and creation entails combining different elemental components into something which can be directly used by people. In other words, circuits serve as a bridge between physical characteristics/devices and ICT. Thus, students studying circuits and telecommunications are equipped with specialized knowledge about the electronics and electrical circuitry used in various electronic devices and passive components, as well as specialized knowledge about the hardware and software used with computers made up of logic circuits.
-
Information Networks
Progress in areas such as artificial intelligence is driving unprecedented advancement in manufacturing. This requires the ability to ascertain data history and subject it to advanced, intelligent information processing. Therefore, students studying information networks are equipped with the specialized telecommunications-related knowledge used to make various devices, circuits and computers connected to sensors, the Internet, etc., run as smart systems.
Subject Introduction
-
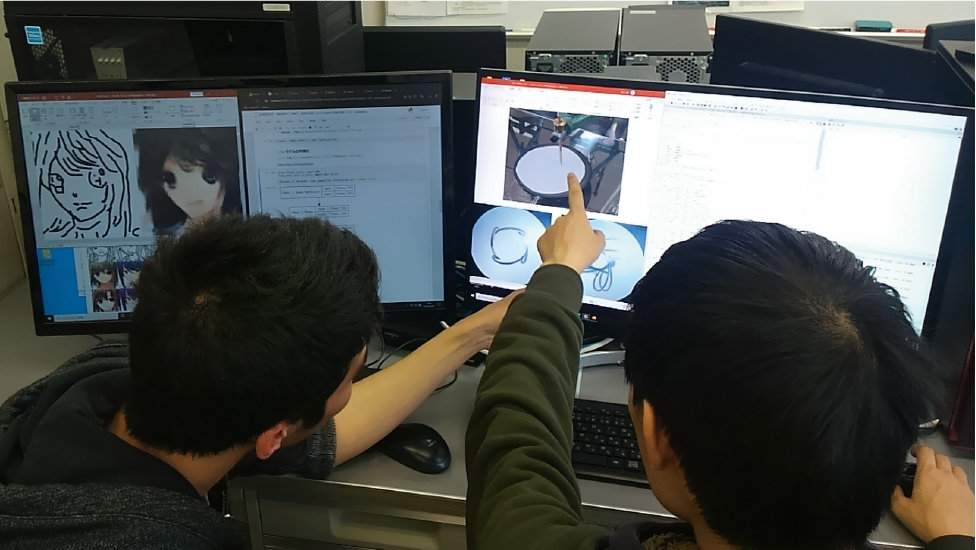

Artificial Intelligence
Through seminars which incorporate real social data, students learn basic concepts in the technology of artificial intelligence, focusing on its use as a means of obtaining useful information from diverse data, specifically via machine learning and deep learning, two areas of particular interest and development in recent years.
-
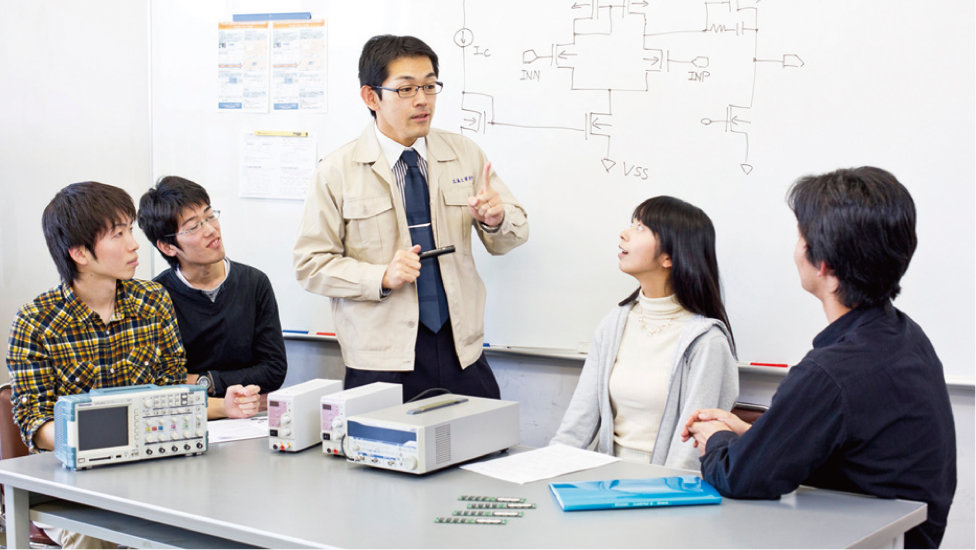

Analog Electronic Circuitry
Classroom instruction is used to equip students with applied knowledge on electronic circuits. Students will gain a deeper understanding of analog electronic circuitry (power supply circuitry, oscillator circuitry, modulation/demodulation circuitry, operational amplifiers) as an important - if often unnoticed - part of our daily life.
-
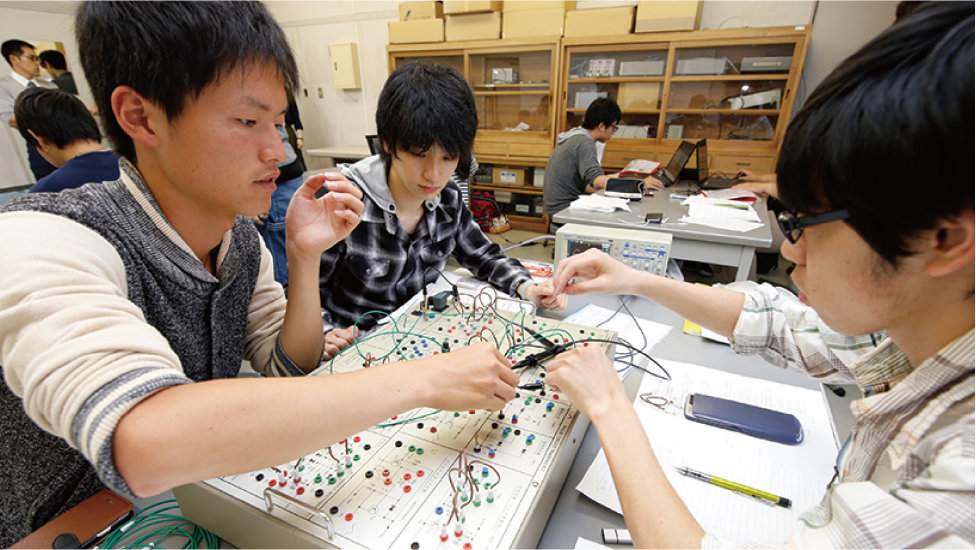
Socio-Practical (example)
Students will acquire specialized knowledge about electronics and information technology, as well as technical instruction which puts theory to the test. Through hands-on experimentation, students will gain a deeper understanding of the proper handling and simulation of devices and equipment.
-
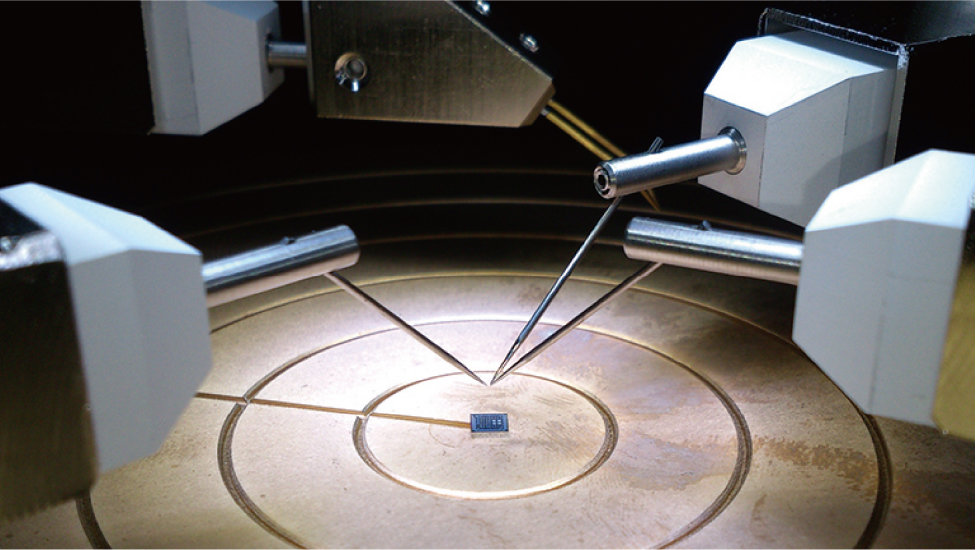
Electronic Devices
In our advanced-information society, the use of IC, LSI and other integrated circuitry is not limited to just computers. Electronic circuitry plays a central role in home electric appliances and automobiles as well, and students will learn about the mechanisms and design methods used to incorporate it.
-
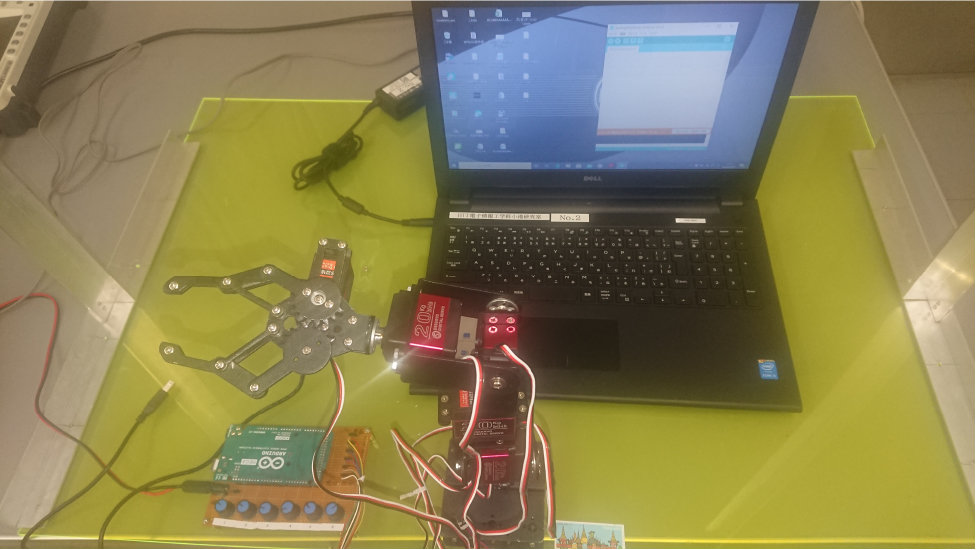
Control Engineering
Students will be equipped with a basic knowledge of Laplace transform definitions and properties, convolution integration, transfer function, block wire fixation, and stability testing in order to help them understand feedback control mechanisms, system modeling and control system analysis and design.
Curriculum
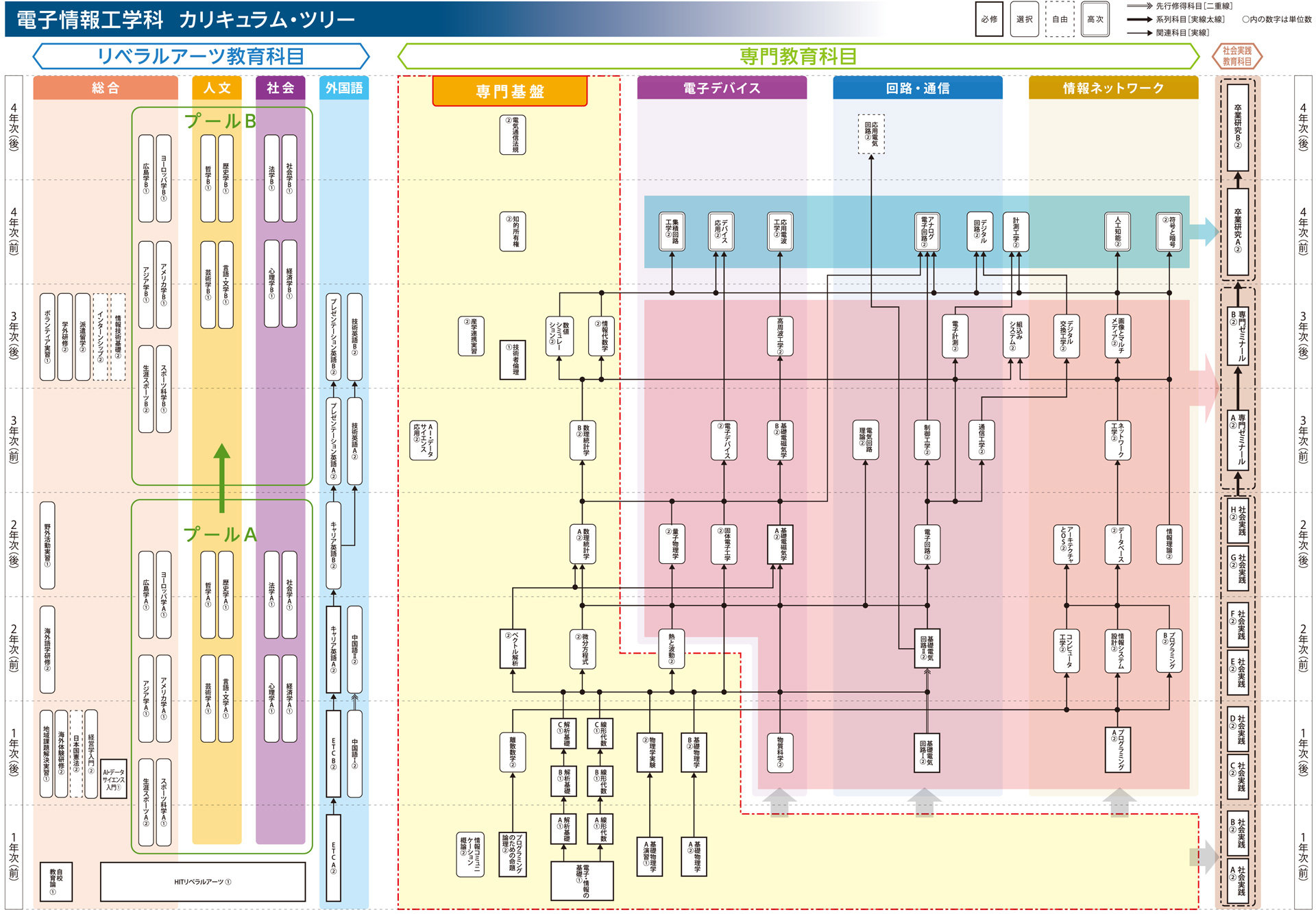
Japanese only






