- Faculty of Engineering
- Department of Electronics and Computer Engineering Department of Electrical Systems Engineering Department of Mechanical Systems Engineering Department of Intelligent Mechanical Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Department of Architectural Engineering
- Faculty of Applied Information Science
- Department of Computer Science Department of Information and Communication Department of Information Systems and Management
- Faculty of Environmental Studies
- Department of Architectural Design Department of Global Environment Studies
- Faculty of Life Sciences
- Department of Clinical Engineering Department of Food Sciences and Biotechnology
- Graduate School
- Major in Intelligent Structure and Functional Science Major in Electrical and Electronic Engineering Major in Mechanical Systems Engineering Major in Civil and Architectural Engineering Major in Information Systems Science Major in Environmental Studies Major in Biological and Biomedical Engineering
Faculty of Engineering
Department of Mechanical Systems Engineering
- Department Introduction
- Education and Research Areas
- Subject Introduction
- Curriculum
- Careers and Further Study
- Department Introduction MOVIE
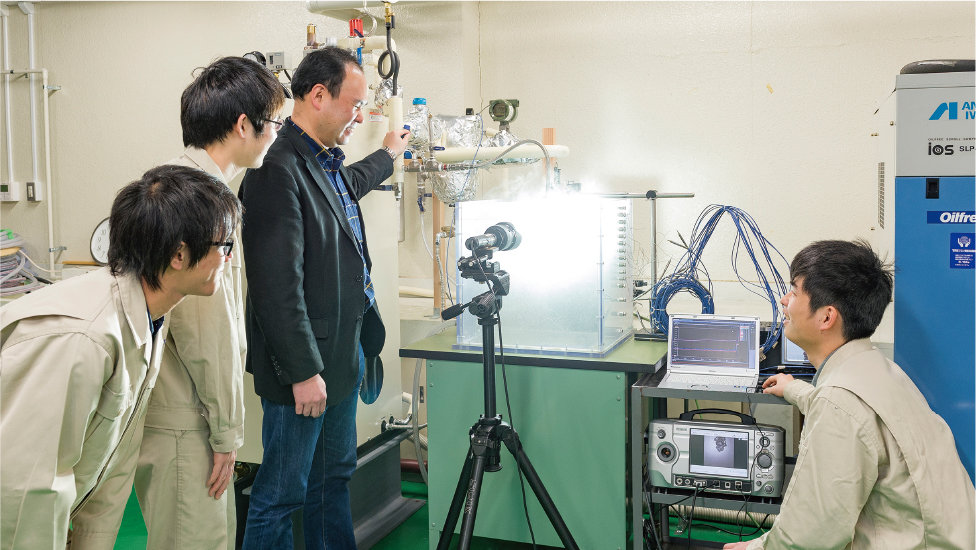
Producing engineers capable of tackling innovative manufacturing challenges.
The content taught in the Department of Mechanical Systems Engineering is applicable in any number of fields, from home electronics to aerospace, automobiles, medical equipment and robotics. Students are equipped with a broad range of expertise and technical skills derived from a basic foundation of mechanical knowledge in the four areas of mechanics, material mechanics, thermodynamics and fluid dynamics and which are necessary for design, material, control system, etc., engineering.
Education and Research Areas
-
Digital Manufacturing
Students learn how to use computers to design and manufacture (CAD, CAM, CAE) machines capable of safely performing prescribed functions. They also learn about materials processing technology and measurement technology, as well as about factory production systems.
-
Advanced Materials
Materials science is the starting point of manufacturing and has a significant impact on mechanical properties, reliability and safety. Students will learn basic theory for steel materials, as well as about the strength characteristics and breaking mechanisms of nonferrous and aerospace materials.
-
Environmental Energy
Students will learn about energy conversion technology used to efficiently extract the energy contained in water and air flow, as well as the thermal energy of combustion and other sources, and convert it into mechanical energy. Students will also learn about the cutting edge of aerospace engineering.
-
Control Systems
Control systems are an indispensable part of modern machines. Students will be equipped with a basic and applied understanding, as well as technical expertise, needed for electrical and electronic systems, control equipment and information systems. Students will also learn about the cutting edge of robotics engineering.
Subject Introduction
-

Design Drawing A and B
Design Drawing A and B will utilize a lecture format to not only teach students how to create drawings but also to read and interpret them. Participants will create their own drawings based upon the mechanical structures, shapes and fabrication methods taught.
-
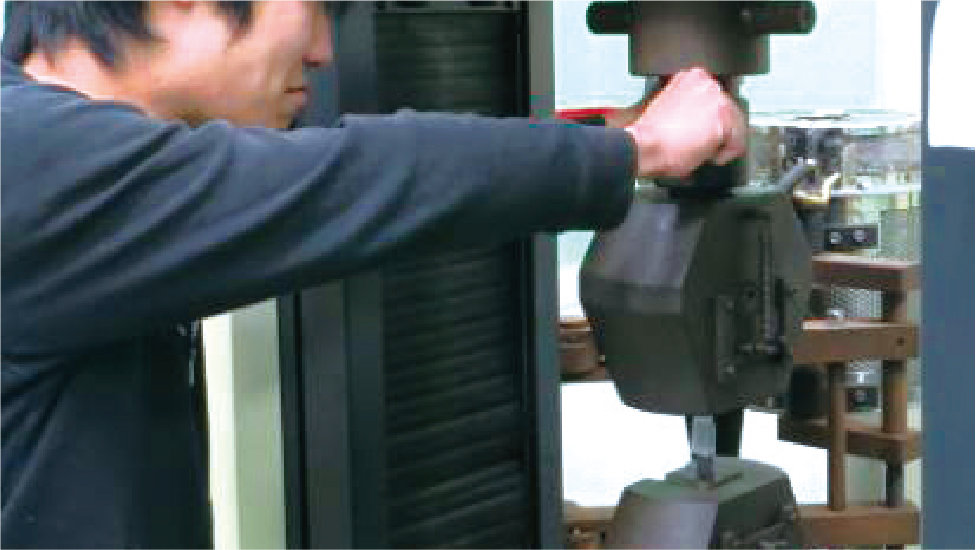

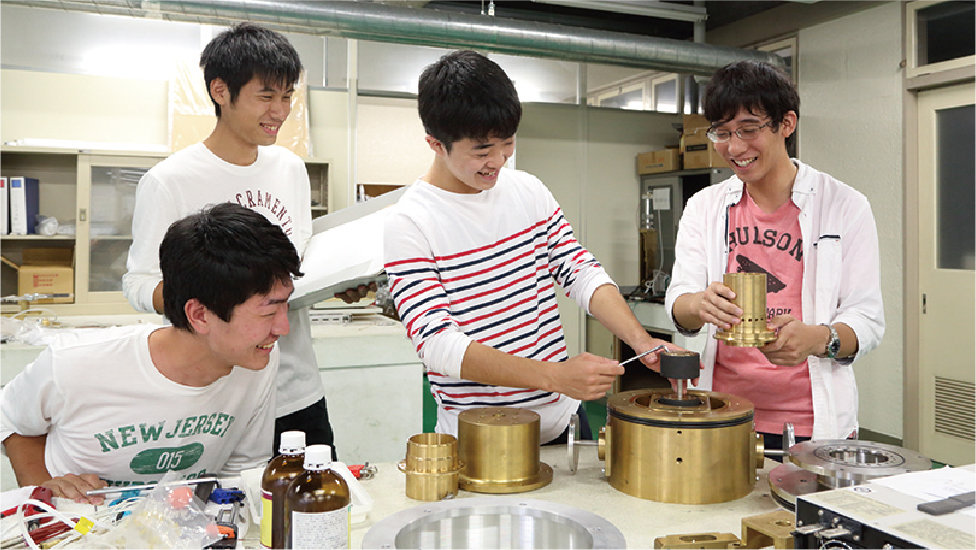
Material Mechanics A and B
These lectures are intended to help students think about how to create safer and more economical mechanical structures by investigating what resistance is produced and what deformation results when force is applied to specific areas of a machine.
-
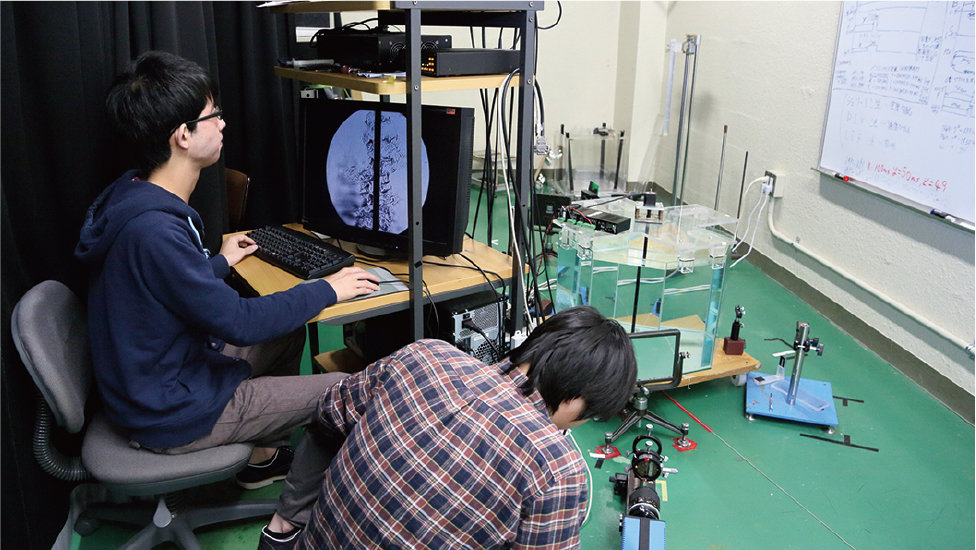

Fluid Dynamics A and B
Fluids, most notably water and air, are associated with flow phenomena on a vast scale which includes our everyday life and everything from microorganisms and soccer balls to airplanes, the ocean, the earth and so much more. Students will learn about the underlying basic principles and laws which all of these have in common.
-

Quality Control
Manufacturers require high-quality, low-cost manufacturing processes. Students will learn the theory and practice of quality control to enable them to identify, evaluate and resolve various challenges faced by manufacturers.
-

Thermodynamics A and B
Students will learn about the essential characteristics of thermal energy and the fundamental laws governing thermal phenomena, as well as gain a deeper understanding of applied thermodynamics by examining such topics as exergy, chemical reactions and combustion, energy conversion, cycle theory-related heat engines, refrigerators/heat pumps and heat transfer engineering.
Curriculum
Japanese only






